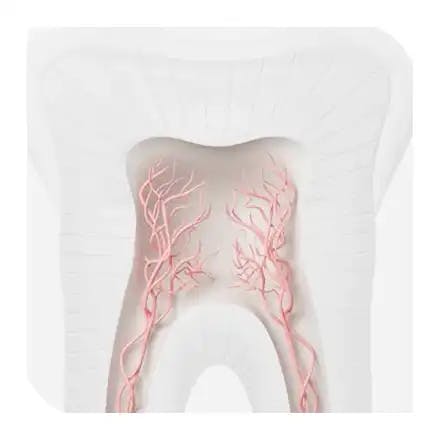
What is acid erosion
Acid erosion is the gradual, irreversible loss of tooth enamel caused by acids from foods, drinks, or the stomach. Enamel is the hardest substance in the body, but frequent acid exposure softens and demineralizes it, making it prone to wear from brushing or chewing.
Common sources include fruits, juices, soft drinks, acidic medications, and gastric reflux. Brushing too soon after consuming acids can speed up the damage. Unlike tooth decay, erosion is not caused by bacteria but by direct acid contact.
Prevention starts with awareness, limiting acidic intake, and gentle brushing habits. Where erosion has occurred, dentists may recommend remineralising treatments to strengthen and protect enamel.
The causes of acid erosion
Having acid-rich diet frequently can put teeth at risk of acid erosion - and it may happen more easily than you think. As few as four acidic food or drink occasions in a single day can be enough to place tooth enamel at risk.
What counts as an “acidic occasion”? Surprisingly, it includes some of our healthier choices, such as fruit and fruit juices.
How acidic are your favourite foods and drinks which are causing enamel loss?
Knowing how acidic foods and drinks are can help you protect your teeth from the effects of acid erosion. Since tooth enamel is made up of minerals that can dissolve when exposed to repeated acid attacks, understanding the pH levels of your favourite foods and drinks is essential. This awareness not only helps prevent further enamel loss but also supports the timely repair of tooth enamel. For example, you might wonder if apples are more acidic than fizzy drinks. The answer may surprise you, and knowing it can guide you towards choices that keep your enamel strong.

What is ph and how is it measured?
pH is a scale from 1 to 14, with values below 7 being acidic and above 7 alkaline. For enamel health, the lower the pH, the higher the risk of damage.
Distilled water is neutral at 7, tomato juice is about 4, and lemon juice around 2. Enamel starts losing minerals below pH 5.5, and frequent exposure can lead to erosion.
Knowing the pH of foods and drinks helps protect enamel and highlights the importance of professional care to keep teeth strong.*
How to protect against acid erosion
Acid erosion occurs when acids from foods and drinks soften the enamel and make it vulnerable to long-term damage. Because enamel cannot grow back once lost, prevention is key
- Consult your dentist: Regular check-ups give personalised advice and care.
- Use Sensodyne Pronamel: Brushing twice daily helps rebuild enamel strength, protect against acid wear, and stay gentle on teeth. *
- Eat smart: Limit frequent acidic snacks, and pair them with non-acidic foods like cheese or milk.
- Use a straw: Sip acidic drinks with a reusable straw and avoid brushing immediately after.
- Consult your dentist:
Regular check-ups give personalised advice and care.
- Use Sensodyne Pronamel:
Brushing twice daily helps rebuild enamel strength, protect against acid wear, and stay gentle on teeth. *
- Eat smart:
Limit frequent acidic snacks, and pair them with non-acidic foods like cheese or milk.
- Use a straw:
Sip acidic drinks with a reusable straw and avoid brushing immediately after.

Reference:
1.West, Nicola X, and Andrew Joiner. Journal of dentistry vol. 42 Suppl 1 (2014): S2-11
2. Malcangi, Giuseppina et al. Bioengineering (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 10,4 472.12 Apr. 2023).